An SF6 circuit breaker is a protective device that uses sulphur hexafluoride gas as an arc quenching medium.
It is the type of circuit breaker used to protect power systems, electrical grids, and distribution stations.
SF6 gas has strong electronegativity and arc quenching properties, making them a better insulating medium than air and oil circuit breakers.
Why is SF6 used in circuit breakers?
SF6 gases are used in circuit breakers because they have high dielectric strength and high cooling effects.
It also has a unique property of quick recombination after arc breaking and is usually a good transfer of heat energy.
That is why it is preferably used in circuit breakers to quench the arc more than air.
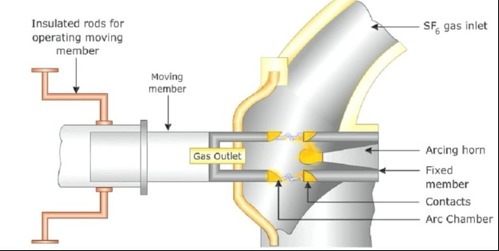
Construction of sulphur hexafluoride gas breaker
The sulphur hexafluoride gas circuit breaker comprises two key parts:
- An interrupter unit
- The gas system
Interrupter unit
The interrupter of this circuit breaker comprises a fixed and movable contact enclosed in a chamber called the arc interruption chamber.
The chamber is then connected to the gas reservoir of the circuit breaker. When the breaker senses fault, it releases the high-pressure gas from the reservoir to cool and extinguish the arc.
Gas system
The gas system comprises a low and high-pressure chamber. It also has a low-pressure alarm and a switch that signals when the gas pressure becomes low.
A low-pressure gas can decrease the dielectric and extinguishing power of the breaker.
And since the SF6 gas is expensive, it is usually reformed after each operation.
Types of sulphur hexafluoride circuit breaker
There are three types of SF6 CB, they include:
- Non puffer type.
- Single pressure puffer type
- Double pressure puffer type
Non puffer type sf6 breaker
This is the first type of SF6 breaker produced without a puffer cylinder. The breaker comprises a gas chamber and an interrupter unit connected by a valve.
The valve is connected to the movement of the breakers’ contacts. Each time the contacts separate, the valve opens to release the blast of SF6 gas, which serves as an extinguisher.
Single pressure puffer type breaker
This type of SF6 breaker usually comes with two fixed contacts and a puffer cylinder.
The movable puffer cylinder filled with SF6 gas acts as a bridge between the two fixed contacts, and is also responsible for making and breaking the circuit when there is a power surge.
Double Pressure Puffer Type SF6 Circuit Breaker
This type of SF6 circuit breaker also uses compressed SF6 gas in a cylinder to quench the arc. But unlike the single pressure puffer type that has two fixed contacts, this one has a fixed and a moving contacts.
However, this type of breaker is no longer in use.
Working principles
In a high-voltage circuit breaker like SF6, current interruption is achieved by separating the contacts in a gas medium.
The sf6 comprises both fixed and movable contacts enclosed in a gas system at a pressure of around 2.8 kg/cm2.
Whenever a fault or short circuit arises, the movable contacts separate, and an arc is struck between them.
Separation of the movable contacts is via an opening valve that allows a high-pressure flow of SF6 gas at 14 kg/cm2 to strike the arc and extinguish them.
Since SF6 gas is electronegative and has a powerful love for free electrons, it absorbs the conducting free electrons in the arc to form immobile negative ions.
Advantages
The advantages of sf6 circuit breakers include:
- They are easier to maintain
- Produces non-hazardous gas
- Produce less noise because of their closed nature.
- Better extinguishers because of their dielectric property.
- Zero risks of a fire outbreak since the gas is non-flammable.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of sf6 breakers are:
Causes greenhouse effect: A greenhouse effect is when gases in the atmosphere such as CO2 trap the energies that supposed to radiate back to space, making the earth warmer.
SF6 gas has a similar effect if released into the environment.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, SF6 is the most powerful greenhouse gas they have assessed, with a global warming potential of 22,200 times that of co2 when compared over a hundred-year period.
It displaces oxygen: Since it is heavier than air, it may displace oxygen. We should always be careful when entering a confined space to avoid the risk of oxygen displacement.
It is expensive because of the cost of SF6 gas
Since the breaker reconditions the gas after every operation, it requires additional equipment for the purpose.
Difference between SF 6 and vacuum circuit breakers (VCB)
| SF 6 CB | VCB |
| Used on high-voltage circuits ranging from 11 kV to 800 kV. | Used on medium voltage circuits ranging from 11 kV to 33 kV. |
| Uses Sulphur hexafluoride gas as an arc quenching medium | Uses vacuum as contact separation medium |
| Mostly used on outdoor appliances | Used majorly on indoor appliances. |
| The short circuit breaking capacity of sf 6 CB is high but not as high as the VCB. | The short circuit breaking capacity of VCB is very high. |
| Hard to install | Easy to install |
| The cost of sf6 breaker is high | VCB is relatively cheap |
| Requires periodic maintenance | Require less maintenance |
| SF 6 breaker is old | VCB is new |
| The pressure of the quenching medium is usually high, about 1500 torr to 1875 torr | The pressure of the quenching medium is usually low about 10-2 torr to 10-6 torr in a vacuum chamber |
Applications
The application of sf6 circuit breakers includes:
- To protect high voltage circuits up to 800 kV.
- Used to protect power grids, generation plants, power transmission and distribution systems.
- Used in capacitor and rectifier circuits
- To protect transformers
- Used in power circuits to protect the lines.
Maintenance
A common problem with SF6 breaker is gas leakage. When leakage occurs, the gas pressure decreases. This reduces the quenching ability of the circuit breaker.
To avoid this, always check your breakers often. You can check that via the pointer of the gas gauge.
If the gauge shows a decrease in gas pressure, subject it to a gas leakage test.
Gas leakage tests require soap water or an SF6 detector. If there is a leakage, consult an engineer for rectification.
You can also fill up the circuit breaker with the new SF6 gas to balance the pressure loss.
Thanks for reading the article.
Related articles
- What is a Molded Case Circuit Breaker?
- How to Replace a Bad Circuit Breaker
- What is a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)?
- What are the Differences Between circuit breakers and GFCIs?
- What is a Motor Protection Circuit Breaker?
- What are the 30 Amp Double Pole Breakers Used for?
- How to wire a Circuit Breaker Box
- What is a 15-amp Circuit Breaker Used for?
- Overview of Square D BDL36100 Powerpact Molded Case Circuit Breaker
- Shunt Trip Breaker: How It Works to Trip a Circuit Breaker.